Polycarbonate plastics are unique and valuable materials at the same time. They are widely used in different industries owing to their outstanding characteristics. They are impact-resistant, optically clear, and thermally stable; thus, polycarbonate plastics are manufactured for high performance in many applications. These thermoplastics span from high-tech microelectronics to low-tech dispersed phase polymers; for example, they range from advanced medical technologies such as devices to lightweight automotive parts and long-lasting building materials. This article reviews the different applications and advantages of polycarbonate plastics. It explains how this material has gained a position as a cornerstone for development and engineering in many industries around the world.
What are the main properties of polycarbonate plastic?
Polycarbonate plastic falls under the category of broad-spectrum material owing to its remarkable properties. Usually, thermosetting polycarbonate is a flame-retardant material with excellent heat resistance and mechanical stability. It is a lightweight material characterized by high tensile and flexural strength. Polycarbonate plastic is also highly transparent, thus possessing the same light-transmitting properties as glass. Moreover, a reinforced polycarbonate can endure temperatures up to 135 degrees Celsius and does not tend to deform. Polycarbonate is a very safe material due to its good dielectric strength and better flame resistance. Factors like ease of fabrication add to the versatility of this material, making it a predominant selection for many industries.
How does polycarbonate’s transparency compare to other plastics?
Polycarbonate is one of the most transparent and common types of plastics, and it allows up to 90 percent of visible light to be transmitted, almost on the glass level. It surpasses the transparency of many other types of plastics, such as acrylics, which may have good light penetration properties but do not have the same impact strength and resistance as polycarbonate. However, unlike plastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, which are usually black or dark blue and have surface textures that are mottled or slightly translucid, polycarbonate possesses optical clarity and a high degree of strength, making it suitable for specific applications like lenses for glasses, shields, and light fittings. It does not lose its optical transparency within a wide range of operating temperatures and environments, making it more functional than other materials of similar usage.
What makes polycarbonate ideal for high-impact applications?
Polycarbonate is suitable for demanding applications because of its high impact and inherent strength. It can be pressed into a stamping die to very high pressure without forming surface cracks or breaking. Still, glass and acrylic do not possess this capability and, as such, cannot be employed in high-pressure environments. In addition, its lightweight and high optical clarity can also be considered for applications requiring visibility and toughness. Due to the excellent high thermal stability of polycarbonate resins and their ability to withstand temperature differences, polycarbonate can protect its structural integrity during rigorous conditions, further enhancing its reputation in protection and structural materials.
How does polycarbonate perform in extreme temperatures?
Polycarbonate is known for its strength and impact resistance, even at higher temperatures. Polycarbonate is thermally stable and can endure temperatures ranging from -40 °F to 248 °F without compromising its optical and mechanical properties. Because of this, polycarbonate is ideal for applications in cold and hot environments and high-temperature ranges, making it suitable for protective gear, industrial coverings, and outdoor sheathing. Our understanding of polycarbonate is enhanced by its ability to withstand exposure to heat without changing its original charged structure.
What are the most common everyday uses for polycarbonate?
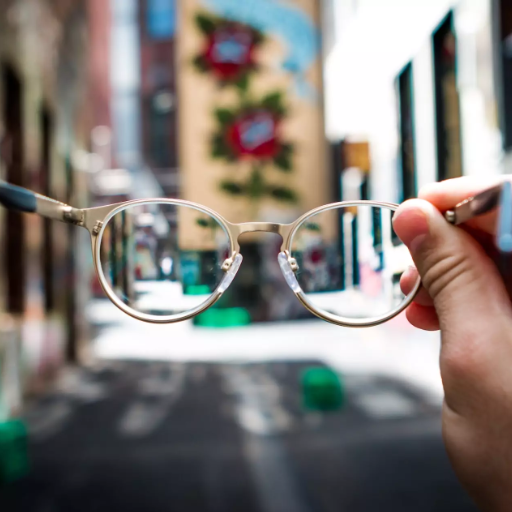

Everyday lenses such as eyeglass lenses are made from Polycarbonate. This material provides ease of use because it is very lightweight but bulky enough to serve its purpose. In addition, it is strong enough to be incorporated into many safety elements, such as helmets and face shields. Many manufacturers use polycarbonate to construct electronic devices due to its strength and capacity to absorb shocks and keep sensitive components safe during transport. In addition, it has a waterproofing effect, which extends its use to reusable water bottles, greenhouses, and lens covers of automotive headlights.
Why is polycarbonate popular for water bottles and food containers?
Polycarbonate is well-known in the food and beverage industry because it is strong, light in weight, and resists impact. It is, therefore, convenient for daily use. Owing to its transparency, users can quickly look at the contents inside the container. At the same time, the material’s resistance to temperature makes it suitable for storing both hot and cold drinks or food. More importantly, polycarbonate is BPA-free in modern-day production, which reduces health and safety risks. Also, polycarbonate is a better alternative to single-use plastics as it has a greater life span and is recyclable, making it more eco-friendly.
How is polycarbonate used in eyewear and safety goggles?
Due to its remarkable impact resistance and lightweight attributes, polycarbonate is found to be applicable to eyewear and safety goggles. It offers adequate protection from fast-moving objects, and hence, chances of injuries are minimized, which is why it has become the required material for safety standards. Due to polycarbonate’s natural UV filtering properties, it helps protect the eyes from damaging sun rays, which is another safety feature. Once coated, these characteristics and the material’s ideal high durability and scratch resistance combinations make polycarbonate suitable for industrial safety and regular glasses.
What makes polycarbonate sheets ideal for greenhouse glazing?
The characteristics of polycarbonate sheets, such as low weight, excellent impact resistance, and good thermal insulation, make them an ideal option for greenhouse glazing. They also provide exceptional light transmission for plants while scattering excess light to reduce hot spots, thereby achieving photosynthetic balance. Moreover, their resistance to harsh climate and UV-resistant coatings guarantee decades of low-maintenance services, which makes them reasonable and practical for greenhouse construction.
How is polycarbonate used in the automotive industry?

The automotive sector extensively uses polycarbonate because it is versatile, strong, and lightweight. Polycarbonate is used to make headlamp lenses due to its ability to resist impacts and transparency. In addition, polycarbonate is used to create panoramic roofs, windows, and other interior parts, which make the vehicle lightweight, thus helping to achieve better fuel consumption. Its strength and resistance to ultraviolet rays also help make the components last longer while looking good and working well.
What automotive parts are commonly made from polycarbonate?
On the other hand, polycarbonate is highly regarded in the automotive industry due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and other valuable characteristics. Its most notable uses include lenses in headlamps because of its excellent clear vision and ability to withstand shocks. Panoramic roofs and windows are another area in which polycarbonate is used to make the car lighter without compromising the structure and giving UV protection. Moreover, polycarbonate creates dashboards and trim panels for the interior to withstand heavy use and scratching while providing excellent design opportunities. All these applications in a vehicle further push the need for better fuel efficiency, performance, and aesthetics.
How does polycarbonate contribute to vehicle safety and efficiency?
Vehicle efficiency and safety are both greatly aided by polycarbonate. The high-impact resistance enhances the structural safety of elements like windshields, headlamp covers, and sunroofs, further guaranteeing that these components can withstand severe impact or even harsh environmental conditions. Moreover, its use of such components tends to increase its overall lightweight nature, which lowers the vehicle’s weight, thus improving fuel efficiency and emissions. Polycarbonate also provides occupants of the car and materials inside with thermal and UV protection, which adds one more reason for its significance to the future of auto construction on the modern design level.
What are the applications of polycarbonate in electronics?

Due to its good electrical insulative properties, high impact resistance, and thermal stability, polycarbonate is well-suited for electronics. It is a good material for crafting circuits, circuit boards, connectors, electrical housing, and switchgear components where safety is a top priority. Because it is both transparent and lightweight, polycarbonate is well suited for use as LED light covers and display panels. In addition, polycarbonate withstands high temperatures and is self-extinguishing, thus making it suitable for sensitive electronic applications.
Why is polycarbonate used in smartphone and laptop casings?
Because polycarbonate is robust, impact-resistant, and lightweight, this material is ideal for laptop and handheld casings. This thermoplastic material can prevent damage caused by drops and shocks, thus ensuring that the devices are intact even for rugged everyday use. Furthermore, the high thermal stability allows the device to endure the amount of heat produced by the components, increasing the device’s safety and lifespan. In addition, polycarbonate can be easily shaped into intricate designs, allowing manufacturers to create slim and compact forms that are lightweight and easy to handle without losing their strength. These features will enable it to be used in entirely new varieties of modern electronic devices.
How does polycarbonate protect electronic components?
Polycarbonate assists in constructing electronic cabinets since it has excellent impact strength, thermal stability and insulation. Due to the mechanical durability of the devices, they are protected from the risk of being damaged when subjected to physical shocks or accidentally dropped while operational. Also, the high temperature that is produced when the device is in operation does not cause damage to it because polycarbonate can withstand high temperatures. Also, because of polycarbonate insulating characteristics, the risk of short-circuiting is reduced, thus preventing potential electrical failures and enhancing the device’s reliability while increasing the lifespan of all electronic components.
What are the advantages of using polycarbonate in construction?

Another reason polycarbonate is an exceptional material for construction is its strength, light weight, and optical clarity. It can be used for all applications requiring strength and durability, like roofing, glazing, and even barriers. Furthermore, because polycarbonate is resistant to the sun’s UV rays, it will not fade or degrade outdoors, allowing it to be effective in outdoor applications for a long time. The material also improves energy efficiency as it provides thermal insulation, is easy to fabricate, and allows for different moldings, making it one of the materials of choice in contemporary buildings.
How are polycarbonate sheets used in roofing and skylights?
Polycarbonate sheets are widely utilized in roofs and skylights because of their remarkable strength, lightweight, and transparency. Their high impact resistance ensures durability against harsh weather conditions, while their UV-blocking coatings protect interiors from harmful rays. Moreover, the features of polycarbonate sheets enable the transmission of light effectively, giving bright and sun-lit rooms, which would benefit greenhouses, production facilities, and housing projects. Their thermal insulation properties also help the space use less energy to maintain the desired temperature. Other than that, because of their flexibility and ease of installation, architects can build unique buildings that are curved or in specific shapes, providing both practicality and beauty.
What makes polycarbonate an attractive option for noise barriers?
Due to its lightweight, rugged, and good noise sample characteristics, polycarbonate material is the best choice for use as a noise barrier panel. Its transparent quality adds aesthetic value and valuable visibility in cities. It withstands harsh weather conditions while ensuring high impact resistance. These properties also make installing and shaping panels easy, making them contemporary noise suppression solutions.
What are the concerns about BPA in polycarbonate plastics?

Polycarbonate construction uses bisphenol A (BPA), which raises concerns about human health and the environment. BPA is notorious for leaching polycarbonate materials when subjected to high temperatures or acidic conditions, and this presents an avenue for human contact with the chemical. Studies have shown that BPA exposure could disrupt endocrine glands and, consequently, hormones, and this can lead to reproductive, developmental, and metabolic disorders. These issues raised concerns by the authorities, which called for the introduction of BPA-free plastic materials for consumer goods.
How has the use of BPA in polycarbonate changed over time?
Changes regarding the regulation and usage of BPA in polycarbonate plastic have, however, been driven by concerns for health and safety. Polycarbonate was first used in food containers, water bottles, and even medical devices as they were durable, heat resistant, and were, most importantly, transparent. Then comes research showing and highlighting the possibility of BPA being an endocrine disruptor. Public and regulatory pressure also increased due to a greater social interest. Many countries placed new restrictions, especially on baby bottles and food packaging. Because of this new demand, new manufacturing methods and alternatives to polycarbonate emerged. Today, the vast majority have started using Tritan or other BPA-free polymers since there is more preference from the social demographic and more stringent regulations. There is also a growing appetite across the globe for safer materials, a state that positively impacts innovation and regulatory change in this space.
What are the alternatives to BPA-containing polycarbonates?
Some reliable substitutes based on polycarbonates containing bisphenol are already on the market. Tritan co-polyester, polypropylene, and stainless steel are carcinogenic-free materials suitable for usage in food and beverage containers. Among the co-polymers, Tritan has excellent clarity and chemical and heat tolerance, which makes it easier to use in place of several products. The other common market material is polypropylene, which is lightweight and used in various applications, such as baby and other reusable bottles. Additionally, stainless steel offers an inert and strong alternative for food and beverage usage, particularly where insulation is needed. These are exceptional materials since they are free of BPA and can meet current safety requirements.
What are the future trends in polycarbonate plastic applications?

Polycarbonate plastic is set to become an authoritative figure across various industries due to its durability, transparency, and lightweight characteristics. Upcoming trends include their use in producing lighter components in automobiles to increase fuel efficiency and in the electronics industry, where they will be used for manufacturing durable casings for devices and optical storage devices. Moreover, the medical industry is also expected to use polycarbonate owing to its sterility and high impact resistance in devices such as syringes and other surgical instruments. New advancements in producing polycarbonate, such as bio-based materials and methods that allow for a more excellent range of recycling, will also be key determinants of how applications will be in the future in adherence to international standards on protecting the environment.
How is polycarbonate being used in 3D printing and additive manufacturing?
The optical clarity, high impact resistance, and temperature tolerance are some of the most admired attributes of Polycarbonate. In recent years, I have learned that the material is increasingly employed in 3D printing and additive manufacturing. Because of the physical and chemical properties possessed by the material, it is suitable for making both robust and functional prototypes, end-use parts, and engineering components. Polycarbonates are ideal for manufacturing light structures while maintaining strength because of their heat resistance and ability to withstand high-temperature environments. Polycarbonate promises strength and reliability in 3D printing applications for the automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries. On the other hand, it is worth noting that sophisticated 3D printers with heated chambers may be needed because of their high melting point and propensity to warp.
What innovative uses for polycarbonate are emerging in medical technology?
On the other hand, polycarbonate is changing the sphere of medical technology by making valuable materials in the form of surgical instruments, casings of medical devices, and implants. The biocompatibility and strength of polycarbonate enable the manufacture of sterilizable and strong equipment, while its transparency helps components such as oxygenators and blood reservoirs. Further, polycarbonate is also being used in 3D-printed custom prostheses and orthoses, which can be designed to meet patients’ individual needs more accurately and faster. These new technologies will be the ones for the next stage of developing more effective and human-oriented approaches to health care.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the physical properties of polycarbonate plastics make them ideal for various applications?
A: Polycarbonate plastics possess several unique physical properties that make them ideal for various applications. These include high-impact strength, transparency, lightweight nature, and durability. Polycarbonate is also known for its ability to withstand high temperatures without cracking or breaking, making it suitable for applications that require thermal stability. Its combination of optical clarity and toughness makes it an excellent alternative to acrylic in many uses.
Q: What are some typical applications for polycarbonate materials?
A: Polycarbonate materials are used in various applications due to their versatile characteristics. Some common uses include: 1. Automotive parts (headlights, interior components) 2. Electronics (smartphone cases, laptop housings) 3. Construction (roofing sheets, skylights) 4. Safety equipment (protective eyewear, helmets) 5. Medical devices (surgical instruments, dialysis machine components) 6. Food storage containers 7. Optical lenses for eyeglasses and cameras These applications take advantage of polycarbonate’s high impact resistance, transparency, and lightweight properties.
Q: What are the key characteristics of polycarbonate that make it suitable for food contact applications?
A: Polycarbonate is widely used in food contact applications due to several key characteristics: 1. It’s FDA-approved for food contact, and 2. High durability and resistance to breakage 3. Transparency, allowing easy visual inspection of contents 4. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for microwave and dishwashing 5. Resistance to staining and odor absorption 6. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for portable food containers. These properties make polycarbonate an excellent choice for reusable water bottles, food storage containers, and commercial kitchen equipment.
Q: What benefits do polycarbonate’s carbonate groups have in their chemical structure?
A: The presence of carbonate groups in the chemical structure of polycarbonate provides several benefits: 1. Enhanced durability and toughness 2. Improved thermal stability 3. Increased resistance to impact and stress 4. Better optical clarity 5. Improved resistance to chemicals and UV radiation These characteristics result from the strong bonds formed by the carbonate groups, contributing to polycarbonate’s unique combination of strength, transparency, and versatility across various applications.
Q: How do different types of polycarbonate grades affect their applications?
A: Different polycarbonate grades are formulated to enhance specific properties for particular applications. For example: 1. Optical grades: Used for lenses and transparent sheets, offering superior clarity and UV resistance 2. Medical grades: Designed to meet biocompatibility standards for medical devices 3. Flame-retardant grades: Used in electronics and construction, offering improved fire safety 4. UV-stabilized grades: Ideal for outdoor applications, resisting yellowing and degradation from sunlight 5. High-flow grades: Suitable for complex molds and thin-walled parts. The choice of polycarbonate grade depends on the application’s specific requirements, such as optical clarity, impact resistance, or chemical resistance.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using polycarbonate plastics compared to other thermoplastic polymers?
A: Advantages of polycarbonate plastics include: 1. High impact strength and durability 2. Optical clarity 3. Heat resistance 4. Dimensional stability 5. Difficulty processing (can be molded, extruded, or thermoformed) Disadvantages include: 1. Higher cost than other plastics 2. Susceptibility to scratching 3. Potential for stress cracking in specific environments 4. Concerns about bisphenol A (BPA) leaching in some applications When compared to other thermoplastics like acrylic or ABS, polycarbonate often offers superior impact resistance and heat tolerance, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Q: How are polycarbonate parts typically manufactured?
A: Polycarbonate parts can be manufactured using various processes, including: 1. Injection molding: Ideal for high-volume production of complex shapes 2. Extrusion: Used to create sheets, films, and profiles 3. Thermoforming: Suitable for creating large, shallow parts from polycarbonate sheets 4. Blow molding: Used for hollow parts like bottles 5. Machining: For custom or low-volume parts 6. 3D printing: Emerging technology for prototyping and small-scale production. The choice of manufacturing method depends on the part’s design, required properties, production volume, and cost considerations. Injection molding is commonly used for many polycarbonate applications due to its efficiency and ability to produce complex shapes.



