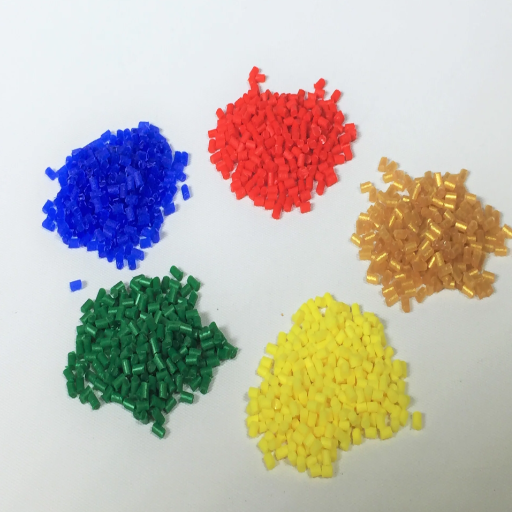
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) is widely used in almost all industries owing to its elastic and thermoplastic properties. The TPE is present in medical devices, consumer products, car parts, etc, and has become an essential part of the manufacturing process today. However, its safety still looms, especially among consumers and those in the industry. This article outlines relevant issues about TPE safety, including its made-up chemicals, any health and environmental effects that might arise, and approved methods that are set out. Whether you are a daily user who wants to know more about everyday products or an industry specialist who wishes to learn more about specific things, this general overview will satisfy your needs and provide logical arguments on TPE safety.
What is TPE, and how is it different from other plastics?

A special class of polymers known as thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) exhibit the elastic properties of vulcanized rubber and the processability and easy remolding features of conventional TPEs. This is possible because the structures of TPEs include both a melted hard part and soft microspheres, thus allowing the TPEs to be injected, molded, and reshaped without any effect on them. Thermoplastic elastomers are advanced elastic materials with superior mechanical, thermal, and environmental properties and a better life span than other thermosetting plastics. They can replace materials like low-modulus polyurethanes, which have replaced rubber in applications requiring adjusted touch and resilience.
Understanding the composition of thermoplastic elastomers
Due to the combination of polymer chains that make up TPEs, they exhibit rubber and plastic characteristics; thus, thermoplastic elastomers composite are block copolymers on a molecular level. They also contain many hard crystalline or semi-plastic domains; the other phase contains amorphous elastomer regions. Hard segments, generally made from polystyrene, polycarbonate, polyamides, and so on, provide mechanical strength for TPEs, while soft segments supply ethylene-propylene rubber and butadiene. Endow easy elastic flexibility. In light of the contradiction between these two structural of TPE, it has reconciled the contradiction in the TPE, which made it possible to behave like simple elastomers but also be processed like thermoplastics, which can be injected, molded, or extruded.
The composite nature of TPE allows one to tailor it to individual preferences. For example, the concentration of hard and soft segments in the block copolymer affects these crosslinking properties. Furthermore, custom applications include stabilizers, fillers, and pigments that can be incorporated during manufacturing to enhance performance or aesthetic value. Because of this controlled compositional variation, it is easy to adapt TPE materials for various applications, from automotive to medical devices.
Comparing TPE to other common plastics like PVC and silicone
There are fundamental differences between thermoplastic elastomers and thermoplastic polyurethanes when comparing them to pvc and silicone in ohm applications. Unlike PVC, which needs to rely on many plasticizers to render it flexible, TPEs are self-elastic, alleviating the ventilating hazards of certain chemicals. Compared to silicone, TPEs are less expensive and can be processed repeatedly, which increases its characteristic properties. For instance, TPEs can be molded in a thermal form. Additionally, TPEs are faster to recommend because they are cheaper than silicone when utilized in large-scale production. This implies that silicone has superior suitability for applications that need contact with the skin due to its strong tolerance to high temperatures, and the TPE application is rewarding in terms of mechanical properties and costs for many applications.
The versatile nature of TPE and its applications
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs), in terms of functionality, are one of the most interesting materials that have, not so long ago, entered the market as they possess unique properties crucial to today’s manufacturing. Due to their elasticity and subsequent thermoplastics, which can be thermally processed, they can efficiently serve the needs of various industries such as automotive, medical, consumer goods, and electronics. For instance, in the automotive industry, due to their incredible strength and being environmentally resistant, TPEs are now widely utilized in sealing systems, gaskets, and soft-touch applications. In the same manner, TPEs are used in the medical industry but for different purposes, such as tubing, seals, and wearable medical devices, because of their biocompatibility and ease of sterilization.
Another important observation about TPEs is that they can be tailored and customized to fit one’s hardness, stiffness, and thermal needs specifications. TPEs are also less damaging to the environment than standard elastomers and can be recycled, making them an attractive option for developing sustainable products. In addition, the formulation of TPEs has been recently improved so that they can be used in high-performance applications, including vibration dampening and over-molded parts where flexibility and strength are required. This means that TPEs will continue to evolve as new applications are invented while existing ones will be improved by incorporating TPEs.
Is TPE safe for human health and the environment?

TPEs might be considered potentially toxic; however, using them for an appropriate purpose is more to ‘the’ risk regarding eco-friendly innovations. Different formulations of TPEs do not consist of PVC and phthalates, which are harmful to use; this minimizes the risk of effective toxication, which, in reverse, threatens mankind and the earth. On the other side, because TPEs are non-biodegradable, they would take longer to decompose, but they are recyclable, which is a positive aspect of using them. Yet, a downside would be that the use of TPE also highly depends on which formulation and application was used. Thus, it remains essential for every individual to check the safety rules and regulations.
Examining the non-toxic properties of TPE
TPEs are applicable across multiple industries and marketable because of the mix and match of their composition, excluding the likes of heavy metals, PVC, and phthalates; in other words, TPEs can be modified and tailored, which in return would make those TPEs non-stubborn and non-toxic. Whenever a TPE is made, a set of rules or standards has been established. For example, it should abide by the REACH and RoHS regulations. This is another reason that TPEs are low risk for human use, depending on what type of TPE they are, in the case of ultra-low allergenic and latex-free TPEs. They can be used for medical appliances and children-friendly items because they would be comfortable. However, the key would be to examine a TPE formulation because it would emphasize whether the TPE could be used per the guidelines.
TPE and phthalates: What you need to know
Phthalates are mostly not found in thermoplastic elastomers, TPEs, which are chemical plasticizers that enhance the flexibility of certain plastics, largely PVC. Many TPE formulations are carefully designed not to use phthalates, which means they are more reliable regarding toxicity levels, for example, medical devices, children’s toys, and food-contact materials. Nonetheless, it is crucial to check the specifications of a particular TPE used by the manufacturer since other formulations may contain additives or plasticizers. Always check the material data sheet, MDS, for compliance with health and safety standards such as those set forth by REACH or FDA to ensure that harmful substances such as phthalates are not present.
Environmental impact of TPE compared to other plastics
However, thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) can be less environmentally concerned than many conventional plastics because they can be reclaimed and reprocessed too often compared to thermosetting plastics. On the other hand, thermosets cannot be melted nor reused, giving them a high material waste rate during manufacturing processes and end-of-life cycles. In addition, the low weight of these materials also enhances energy efficiency in applications such as automotive parts since there is a decrease in fuel requirements. On the contrary, the environmental performance of TPEs is intimately related to the specification of their formulation and the recycling policies in a particular industry. While it has been noted that TPEs may be easier on the environment than some plastics, further research is needed to focus on producing 100% biodegradable or bio-based TPEs.
What safety standards govern TPE manufacturing and use?
International and national safety regulations are related to TPE’s manufacture and usage. The ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 measures are critical to guaranteeing the quality and environmental protection of the processes. BSE Medical Devices standards are set by ISO 10993 for the molding and testing thermoplastic elastomers for medical purposes. In the same way, the legislation in the United States concerning food and medical applications of thermoplastic elastomers is regulated by the FDA and the Title 21 CFR. Compliance with these norms guarantees that the product is safe, environmentally friendly, and meets the legal requirements for a given sector.
Understanding TPE safety regulations and certifications
As in the case of other internet polymer blends, the safety standards and test certificates of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) emphasize the offense of the chain of custody of the polymer, its production, and disposal. Important in this sense are the phthalates and heavy metals limit regulation using the REACH specifications, as OPA TE documents do restrict this kind of presence in TPEs in the EU. This guarantees the health and environmental requirements associated with its production and consumption are observed.
Likewise, in the USA, the TPEs employed, for example, in food contact, in combination with medical devices, and with pharmaceutical packaging, are reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration under regulations such as FDA CFR Title 21. This says that materials employed should not enable extraction of substances that may be hazardous to health, such as leaching to food or the human body, and such provisions, above all, enhance public safety.
Moreover, TPE materials and products can be subject to certification based on third-party standards such as ISO 10993. This assessment selection applies mainly to the biocompatibility of medical grade materials because TPES must be medically safe in any application area close to where they will be in contact with biological tissues or fluids for an extended period. Another commonly found certification is RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), which restricts certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, enabling safe TPEs to substitute materials in different sectors.
These norms and certifications further ensure that a quality system that ensures humans can consume TPEs and not at the cost of the environment suits the requirements of the global marketplace efficiently.
How manufacturers ensure the safety of TPE products
Manufacturers conform to international standards and conduct thorough testing to protect TPE products. To ensure safety, TPE materials are routinely assessed for crucial properties such as tensile strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. We also conduct compliance and pollution assessments to support essential regulations like RoHS, REACH, and FDA without toxic substances. Implementing quality measures at every production level and cost-effective testing technologies enables us to provide dependable, safe, and compliant TPE products.
TPE in children’s products: Special safety considerations
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) in children’s products must meet strict requirements in their formulation to be safe, long-lasting, and suitable for extended use. Choosing phthalate and BPA-free materials is preferable to minimize further exposure to harmful chemicals. Apart from that, TPEs must also meet some regulations such as EN 71-3 standards and CPSIA for toy safety to ascertain that it is safe for the children. Products like toys and teething rings are designed to be bitten, chewed, and handled roughly, so the material should be wear-resistant. The items are also flame-resistant and free of allergens, which is necessary for selected governing bodies and public safety. In short, proper research and adopting a good TPE mix encourages manufacturers to believe these items are safe, long-lasting, and effective under many scenarios.
How does the manufacturing process of TPE affect its safety?
The safety of TPE is affected considerably by how it is made in that it defines the properties of the material in terms of its purity and uniformity as well as the level of mechanical properties of the material. All the quality controls are exercised during the production stage to ensure that the finished products do not possess harmful substances like heavy metals or residual monomers. Uniform characteristics of a material are reached through sophisticated compounding combined with precise temperature and pressure control during processing, both of which minimize the formation of weak points or contamination. Furthermore, compliance with regulatory specifications, such as FDA or REACH regulations, allows the TPE to be suitable and safe for the intended uses, whether medical, consumer, or industrial.
Overview of TPE production techniques
Processes such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding are basic thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) production techniques. The production process starts with an appropriately selected base polymer and, in most instances, is a blend of hard thermoplastic segments and soft elastomer components. The compounding step is essential because various additives, such as fillers, stabilizers, and colorants, are added to improve the polymer’s toughness, UV resistance, and flexibility, among other characteristics.
Producing TPE products has been streamlined and made efficient through injection molding. This is done by melting the TPE material and forcing it into a mold cavity through a designed inlet port under a predetermined temperature and pressure condition. Extrusion, on the other hand, is more suited for the making of continuous products which include such as pipes, profiles or sheets, in the extrusion process, TPE is also heated to a to a molten form and then exerted through a die for the production of shapes of uniform cross section.
Each technique emphasizes strict control of the process, such as the mixing, melting, and cooling of the product so as not to alter the material’s properties. Advances such as multilayer co-injection molding and multi-material structural fabricating can produce intricate and functional structures, extending TPE applications in auto and consumer electronics, among other industries. The use of high-quality machines and best manufacturing practices aid TPE manufacturers in ensuring maximum productivity without compromising the quality of the final product.
Potential risks in TPE manufacturing and how they’re mitigated
A loss in the integrity or uniformity of the end product may be attributed to material contamination, one of the significant risks associated with TPE manufacturing. In this regard, we have implemented raw material inspection procedures and further guarantee a clean working environment by frequently overseeing the condition of the equipment. Temperature and processing can be challenging as getting them right is usually a nightmare, and any discrepancy often results in a sub-par product. We approach this concern with highly developed monitoring devices integrated into the TPE processing apparatus and observing the established procedures. Lastly, the generation of waste and its effect on the environment are concerns addressed by recycling materials and environmentally friendly modes of production as acceptable by the law.
The role of quality control in ensuring safe TPE products
It is essential to understand the impact of quality control on the safety and functionality of thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) for different possible uses. It involves extensive testing and inspection throughout the manufacturing cycle to assess possible flaws, material variations, or impurities. Specific methods like thermal analysis and tensile tests investigate TPE’s thermal and mechanical characteristics. The authorities’ insistence on products meeting international criteria such as ISO and REACH means that these products are non-harmful and effective. Reasonable quality control reduces the chances of product failure, increases the product’s ability, and, most importantly, assists in complying with legal and customer satisfaction.
What are the common uses of TPE, and are they safe?
In packaging, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are the most used due to the requirements of safety, strength, and other desired properties. For instance, TPE is widely used in car parts such as seals, gaskets, trims, medical tubing, syringes, grips, handles of many products, and shoes and sports goods. It is considered safe if TPE meets the safety requirements of ISO and REACH. These controls ensure that TPE does not contain dangerous contaminants, is not hazardous to individuals and nature, and can be used in household and industrial items.
Exploring TPE applications in consumer goods
Due to the combination of flexibility, durability, and appeal, traditional TPEs in the consumer goods markets have had significant success. They are widely used in soft-touch toothbrush grips, handsets, smartphone cases, and kitchen plastic utensils. With TPEs, color and texture variations provide an option to personalize the product, making it more pleasing to the user and the market. Also, their application is being widened as versatile functionalities, including wearables and fitness equipment, which are easier and safer due to their lightweight and hypoallergenic properties. In addition, the combination of TPE reusability and the growing sentiment among consumers about using green and sustainable products are changing the praises of TPE for manufacturers striving to lessen their carbon footprints. These merits emphasize the importance of TPE in the strategy of many manufacturers of modern consumer goods.
Safety of TPE in food contact materials
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are considered food-grade if manufactured within specific guidelines. I have searched trustworthy sources, and it is evident that TPEs comply with FDA and EU requirements, provided that the required migration limits are met, ensuring that no food or harmful substances come into contact with the seal. This stability and low toxicity make them suitable for various applications, including seals, gaskets, and container coatings. Nevertheless, manufacturers should conduct testing and certification to prove they are safe for food contact applications.
TPE in medical devices: Balancing flexibility and safety
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) have critical applications in making medical devices as they are rubber and plastic simultaneously. These devices can be molded explicitly into complex shapes that are suited to tubes, syringes, plungers, and some orthopedic devices. Most importantly, TPEs have passed stringent ISO 10993 and USP Class VI requirements to be accepted as biocompatible and hypoallergenic. The non-latex composition of TPEs also helps minimize allergic reactions in allergy-prone surgical rooms. Furthermore, their ability to withstand sterilization through autoclave, ethylene oxide, or gamma sterilization demonstrates their reliability in making reusable and single-use medical devices. Therefore, for TPEs to comply with regulations, there is a need for comprehensive testing for performance in clinical scenarios, which is a priority when considering patient welfare.
Can TPE be recycled, and how does this impact its safety profile?

The safety and environmental profile of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) is improved because they can be easily recycled. This characteristic is also due to nature since TPEs are thermoplastics so that they can be reshaped and reused without notable deterioration of their main properties. Such recyclability lowers the waste of submitted materials and the environmental impact when used in medical and industrial applications. On the other hand, to safeguard the safety profile of TPEs post-recycling, careful production control measures must be observed during recycling. These ensure that the material has the desired biocompatibility and mechanical integrity level and complies with regulations, particularly in direct contact with patients.
The recyclability of TPE compared to other plastics
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are much more advantageous than many traditional plastics due to their recycling ability. Because of curing, thermosetting plastics develop irreversible chemical alteration. TPEs’ thermoplastic characteristic means that they can be remolded and reshaped many times without significant loss of performance. This feature makes TPEs more efficient, reduces material loss, and improves the circular economy.
Unlike conventional plastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), TPEs offer extraordinary elasticity and processing ease. Even though PE and PP are widely employed, their inflexible structure hampers the range of their applications. In contrast, TPEs are still remarkably elastic and can substitute for numerous materials in various applications that aid the minimization of new plastic production.
In addition, TPEs are particles that have a much softer impact in terms of disposal due to their low reliance on recycling compatibilities than other plastic wastes such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polystyrene (PS). Also, because of advanced production technologies, it is now possible to manufacture TPE compounds that contain recoverable material but do not entail the loss of essential characteristics such as biocompatibility and durability. Therefore, TPE represents a profitable, efficacious, and environmentally friendly solution in industries that face ecological challenges.
How recycling affects the safety and quality of TPE
The safety and quality of the TPE can significantly benefit from incorporating the recycling of materials by ensuring the effective sourcing and treatment of the recycled materials. Recycled content is required to undergo stringent quality control operations to protect the key end-use characteristics of the product, such as elasticity, durability, and biocompatibility. Impurities in the recycled feedstock could affect performance or present safety issues, but improvements in the sorting and purification processes have tended to reduce those risks. Manufacturers can use this recycled material without affecting the quality standards and also work towards achieving sustainability goals.
Environmental benefits of using recyclable TPE
Adoption of recyclable TPE results in profound environmental advantages through waste disposal and natural resource saving. Treating TPE materials enables using less virgin raw materials, which in turn helps save energy needed for production and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, using recyclable TPE promotes the concept of circular economy since it allows the same materials to be used many times without affecting performance. This technique not only alleviates the pressure on landfills but is also consistent with the global approach to dealing with issues brought about by environmental destruction.
What precautions should consumers take when using TPE products?

Integrating TPE products into your inventory can be satisfactory in many aspects; however, before marketing or using these products, ensure that the requirements for application instructions, maintenance, and disposal are always met. The temperatures shouldn’t be too hot or too cold, and the use of harsh chemicals should be avoided while cleaning TPE. Customers need to understand that the application of TPE should have been approved and certified to mitigate any safety concerns associated with food contact or medical purposes. Lastly, the disposal or recycling of such items should be done responsibly to enhance the environment and the sustainability of its products.
Tips for identifying safe TPE products
On the other hand, to determine the credibility of the TPE goods, understanding that the FDA, REACH, or RoHS certifies them will be very important since each certifies the level of safety required and adherence to the set standards. Always look for safety standards comprehensively defined in packaged items or manufacturer documents; this will ensure safety primarily when the TPE goods are used in contact with food substances or medical devices. Numerous reputable manufacturers define their material sources and make their production processes visible, seeking their products more so if the need arises. For most of the TPE additives, the risk of toxicity is usually low or not present at all; thus it is wise to look for materials that have elaborate instructions on how to use them as well as on the risks they pose, this will go a great way in ensuring safety.
Proper care and maintenance of TPE items
TPE items can’t be maintained without washing, so I use warm water and soap-free of harsh chemicals or abrasive material to preserve the surface. TPE products should also not be placed in direct sunlight as the exposure may damage them; thus, I keep them in cool and dry areas during storage. When dealing with items designed especially for medical applications or food contact, I also follow the sterilization guidelines set by the manufacturer to avoid contamination. Keeping a check on wear and tear on items allows me to replace them in case they have any functionality or safety concerns, so I check for that as well.
When to replace TPE products for optimal safety
The guidance for replacing TPE products includes visual examination and performance measurements. The most critical indicators in this case are the presence of cracks, cuts, indents, or any other deformations that might result in detrimental effects. Replacing a TPE product that gets sticky, discolored, or loses elasticity will also be helpful because it may worsen with time, environmental exposure, or poor maintenance. In line with this, TPE products used in health care, food handling, and other safety-sensitive areas should stick with the manufacturer’s recommended replacement frequency since these estimates consider normal wear and tear and the necessary regulatory requirements. A periodic assessment of use-related factors to evaluate the product condition factors is performed to help prevent compromising safety and efficacy.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is TPE, and how is it used?
A: TPE, or Thermoplastic Elastomer, is a versatile material that combines the properties of plastic and rubber. It’s used in various applications, including yoga mats, automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods. TPE is often chosen for its flexibility, durability, and eco-friendly characteristics.
Q: Is TPE safe for human use?
A: Yes, TPE is generally considered safe for human use. TPE doesn’t contain harmful substances such as phthalates or BPA, unlike other materials. Its safety profile has been well-established, making it a safe choice for products that come into direct contact with skin, such as TPE yoga mats.
Q: How does TPE compare to natural rubber in terms of safety?
A: TPE is often considered safer than natural rubber for several reasons. It doesn’t contain latex, which can cause allergic reactions in some people. Additionally, TPE is more resistant to degradation and doesn’t release harmful compounds over time, making it a more stable and safe material for long-term use.
Q: What makes TPE safe to use in various applications?
A: TPE’s safety stems from its chemical composition and manufacturing process. It is a type of plastic that doesn’t require vulcanization or curing agents, which can sometimes introduce harmful substances. TPE is also highly chemical resistant and can be formulated to meet specific industry safety standards.
Q: Are there different types of TPE, and are they all safe?
A: Yes, there are several types of TPE, including SBS, SEBS, TPO, and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane). While the safety profile may vary slightly between types, all TPEs are considered safe when properly manufactured and used as intended. Choosing the right kind of TPE for each specific application is essential to ensure optimal safety and performance.
Q: Is TPE toxic or harmful to the environment?
A: TPE is not considered toxic to humans or the environment. It’s often regarded as eco-friendly because it can be easily recycled and doesn’t release harmful chemicals during its lifecycle. However, like all plastics, proper disposal and recycling are essential to minimize environmental impact.
Q: How does the manufacturing of TPE contribute to its safety?
A: TPE is manufactured using processes that ensure its safety. It doesn’t require vulcanization or the addition of potentially harmful curing agents. The production methods allow for precise control over the material’s composition, ensuring no unwanted substances are introduced. This clean manufacturing process contributes significantly to TPE’s overall safety profile.
Q: Can TPE be safely used in medical applications?
A: TPE is often used in medical applications for its safety and versatility. Many types of TPE can be formulated to meet strict medical-grade standards, including biocompatibility requirements. It’s used in various medical devices, tubing, and equipment where safety is paramount, confirming that TPE is safe for human contact.



